Historical Overview of NATO Membership

Nato members – The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was founded in 1949 as a collective security alliance between the United States, Canada, and several Western European countries. The alliance was created in response to the perceived threat of Soviet expansionism following World War II. NATO’s primary goal was to deter Soviet aggression and maintain stability in Europe.
As tensions escalate, NATO members have been seeking strategic guidance from experts like George Stephanopoulos , who has extensive experience in international relations. Stephanopoulos’s insights have proven invaluable in shaping the alliance’s response to the evolving geopolitical landscape, ensuring that NATO members remain prepared to address the challenges of the 21st century.
Key Milestones in NATO’s Expansion
NATO has expanded several times since its founding. The first major expansion occurred in 1952 when Greece and Turkey joined the alliance. In 1955, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) joined NATO. In 1982, Spain joined the alliance. In 1999, Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic joined NATO. In 2004, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined the alliance. In 2009, Albania and Croatia joined NATO. In 2017, Montenegro joined the alliance. In 2020, North Macedonia joined the alliance.
NATO members have been eagerly anticipating the outcome of the Biden interview , hoping for a clear direction on the alliance’s future. The interview shed light on Biden’s plans for strengthening NATO’s unity and collective defense capabilities, reinforcing the importance of transatlantic cooperation and the need for a united front against emerging threats.
Timeline of Countries Joining and Leaving NATO
- 1949: United States, Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, United Kingdom
- 1952: Greece, Turkey
- 1955: Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany)
- 1982: Spain
- 1999: Poland, Hungary, Czech Republic
- 2004: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia
- 2009: Albania, Croatia
- 2017: Montenegro
- 2020: North Macedonia
Current NATO Membership

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) currently comprises 30 member states, spanning North America and Europe. The organization’s membership has expanded over the years, with the most recent additions being Montenegro in 2017 and North Macedonia in 2020.
NATO Members by Region
NATO members can be grouped into two main regions:
- North America: United States, Canada
- Europe: Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, United Kingdom
NATO Members by Alphabetical Order
- Albania (2009)
- Belgium (1949)
- Bulgaria (2004)
- Canada (1949)
- Croatia (2009)
- Czech Republic (1999)
- Denmark (1949)
- Estonia (2004)
- France (1949)
- Germany (1955)
- Greece (1952)
- Hungary (1999)
- Iceland (1949)
- Italy (1949)
- Latvia (2004)
- Lithuania (2004)
- Luxembourg (1949)
- Montenegro (2017)
- Netherlands (1949)
- North Macedonia (2020)
- Norway (1949)
- Poland (1999)
- Portugal (1949)
- Romania (2004)
- Slovakia (2004)
- Slovenia (2004)
- Spain (1982)
- Turkey (1952)
- United Kingdom (1949)
- United States (1949)
Expansion and Future Prospects: Nato Members
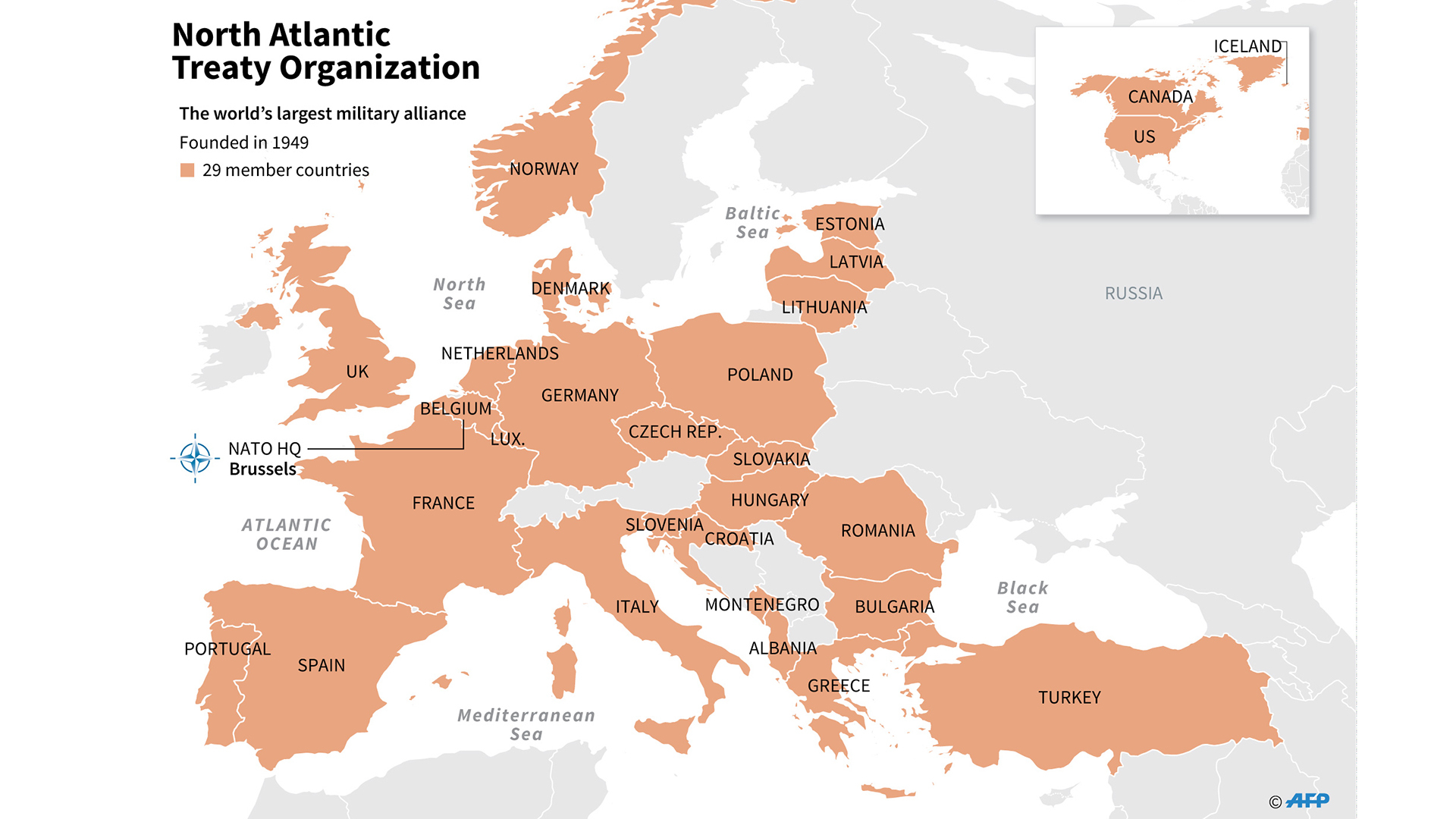
NATO has undergone significant expansion since the end of the Cold War. In 1999, Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic joined the alliance. In 2004, seven more countries joined: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia. In 2009, Albania and Croatia joined, and in 2017, Montenegro joined.
The expansion of NATO has been a controversial issue. Some argue that it has helped to stabilize Europe and deter Russian aggression. Others argue that it has provoked Russia and increased tensions between the two sides.
Potential Implications of Further NATO Expansion, Nato members
The potential implications of further NATO expansion are complex. On the one hand, it could help to further stabilize Europe and deter Russian aggression. On the other hand, it could further provoke Russia and increase tensions between the two sides.
The decision of whether or not to expand NATO is a complex one. There are a number of factors that need to be considered, including the security interests of the countries involved, the potential for further conflict, and the impact on relations with Russia.
Countries Considering Joining NATO
There are a number of countries that are considering joining NATO. These include Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Macedonia, and Ukraine. However, each of these countries faces challenges in joining the alliance.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is still recovering from the Bosnian War of 1992-1995. Georgia is involved in a conflict with Russia over the breakaway regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Macedonia has a long-standing dispute with Greece over the name of the country. Ukraine is facing a Russian-backed separatist movement in the eastern part of the country.
Despite these challenges, the countries considering joining NATO are all committed to the alliance’s values of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law. They believe that membership in NATO would help to protect their security and promote their democratic development.