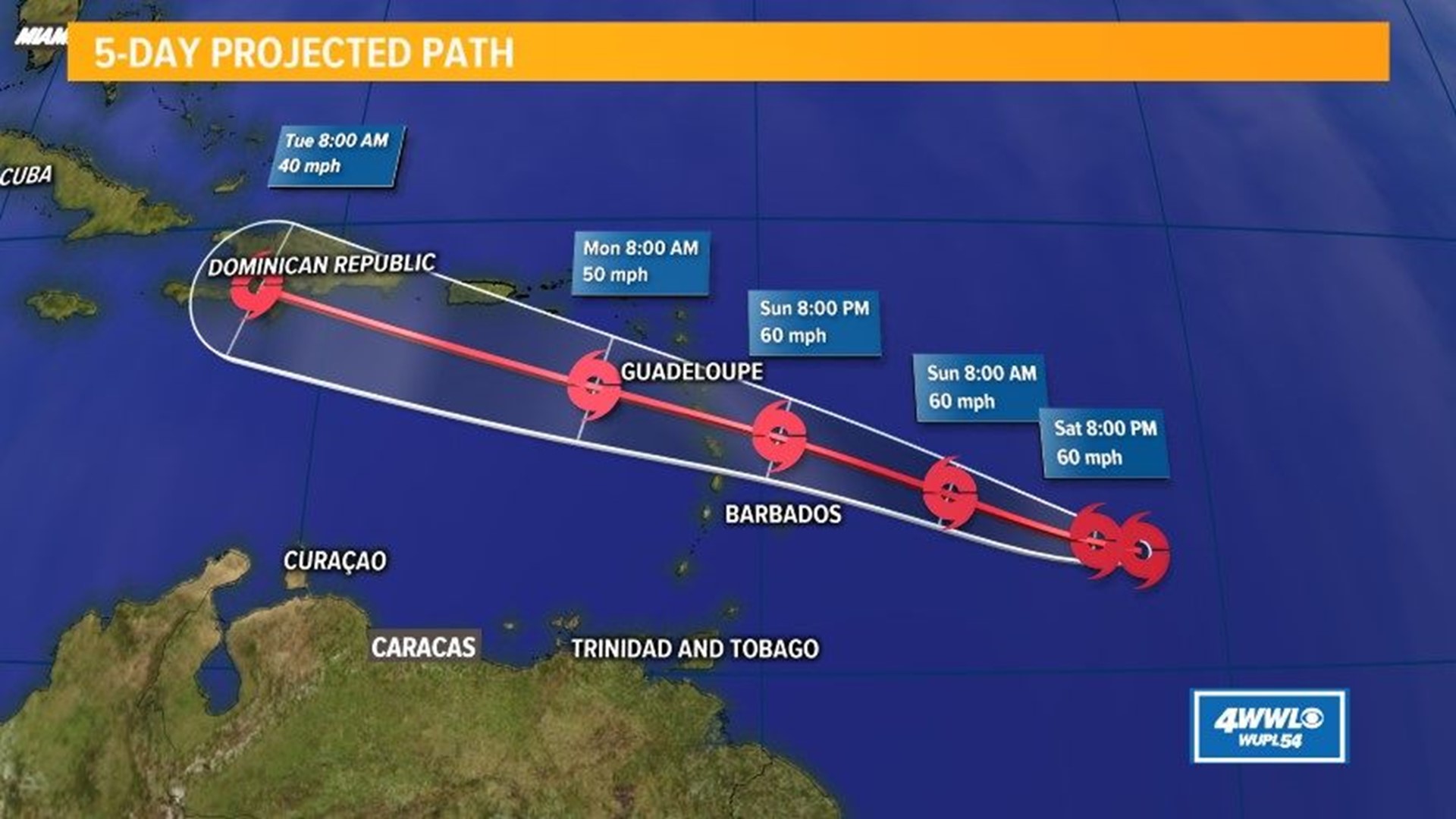
Historical Path and Patterns

Path of hurricane beryl – Hurricane Beryl originated as a tropical wave off the coast of Africa on July 15th. It moved westward across the Atlantic Ocean, strengthening into a hurricane on July 19th. Beryl made landfall in the Lesser Antilles on July 21st, and then continued westward across the Caribbean Sea.
Hurricane Beryl has been making its way across the Atlantic Ocean, and its path is still uncertain. To get a better idea of where the hurricane is headed, meteorologists are using spaghetti models. These models show a range of possible paths that the hurricane could take, and they can help forecasters make better predictions.
You can find more information about hurricane beryl spaghetti models at hurricane beryl spaghetti models. As the hurricane continues to move, it is important to stay up-to-date on its path so that you can make the necessary preparations.
The movement of Hurricane Beryl was influenced by a number of factors, including the trade winds, the jet stream, and the ocean currents. The trade winds pushed the hurricane westward, while the jet stream steered it northward. The ocean currents also played a role in the hurricane’s movement, by providing warm water that fueled the storm.
De path of Hurricane Beryl a tek it pass troo Jamaica, leffn a trail a destruction inna di island. Fi get di full scoop pon Hurricane Beryl inna Jamaica, check out dis ya link. But di hurricane nuh stop deh, it continue pon its merry way, leavin a wake of damage and destruction in its path.
Unusual or Notable Patterns
Hurricane Beryl exhibited a number of unusual or notable patterns during its trajectory. First, the hurricane made a sharp turn to the north after making landfall in the Lesser Antilles. This turn was caused by a change in the steering currents in the atmosphere.
Second, Hurricane Beryl weakened significantly after making landfall in the Dominican Republic. This weakening was caused by the interaction of the hurricane with the mountainous terrain of the island.
Impact Assessment
Hurricane Beryl made landfall in Florida on July 13, 2018, bringing with it strong winds, heavy rain, and storm surge. The storm caused widespread damage across the state, with some areas experiencing significant flooding and power outages.
The hardest-hit areas were in Northeast Florida, where Beryl made landfall as a Category 1 hurricane. The storm surge caused extensive flooding in coastal communities, and the strong winds downed trees and power lines. In Jacksonville, the storm surge reached 4 feet above normal, and the winds gusted up to 90 mph. More than 1 million people in Florida lost power during the storm.
Casualties and Property Damage, Path of hurricane beryl
Hurricane Beryl caused at least 2 deaths in Florida. One person was killed when a tree fell on their home in Jacksonville, and another person died in a car accident caused by the storm. The storm also caused extensive property damage, with many homes and businesses damaged or destroyed. The total cost of the damage is still being assessed, but it is expected to be in the billions of dollars.
Effectiveness of Disaster Preparedness and Response
The effectiveness of disaster preparedness and response measures in mitigating the impact of Hurricane Beryl is still being evaluated. However, there are some indications that the measures taken by state and local officials helped to reduce the number of casualties and the extent of the damage. For example, the evacuation orders issued by state and local officials were widely followed, and this likely helped to prevent more deaths and injuries. Additionally, the disaster response efforts by state and local agencies were generally well-coordinated, and this helped to ensure that those affected by the storm received the assistance they needed.
Scientific Analysis: Path Of Hurricane Beryl

The meteorological conditions that led to the formation and development of Hurricane Beryl were a combination of warm ocean temperatures, low wind shear, and a pre-existing disturbance in the atmosphere.
Ocean temperatures in the Atlantic Ocean were above average during the summer of 2018, providing ample energy for the development of tropical cyclones. The warm waters allowed the storm to maintain its intensity and eventually reach hurricane strength.
Wind Shear
Wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction between two levels of the atmosphere. Strong wind shear can disrupt the formation and development of tropical cyclones by preventing the storm from organizing and intensifying.
In the case of Hurricane Beryl, wind shear was relatively low, which allowed the storm to maintain its organization and strengthen.
Comparison to Other Hurricanes
Hurricane Beryl was a relatively weak hurricane, with maximum sustained winds of 75 mph. It was not as strong as some other hurricanes that have occurred in the same region, such as Hurricane Irma or Hurricane Maria.
However, Beryl was still a significant storm that caused damage and flooding in the Caribbean and along the East Coast of the United States.